The Easy Guide To Automating Power BI Variance Analysis
[ad_1]
Welcome to the wild world of finance, where numbers dance and data tells tales. Today, we’re going to dig into the art of Power BI Variance Analysis. If you’ve got your curiosity hat on, let’s jump right in!
What is Power BI?
Think of Power BI as your trusty sidekick in the chaotic realm of business analytics. Crafted by Microsoft, this tool is all about turning data into eye-catching visuals and helping you make sense of it all. Imagine having a kaleidoscope for numbers—Power BI does just that.
It’s like having a personal assistant who not only keeps your data organized but also makes it look good. From creating dynamic reports to interactive dashboards, Power BI turns the mundane into the magical.
Understanding Variance Analysis
Now, let’s talk variance analysis—the Sherlock Holmes of financial investigations. This is where we dig deep to compare what’s expected versus what actually happened. Is there a gap? Absolutely. And variance analysis is here to tell us why.
It’s not just about spotting errors; it’s about uncovering the story behind those numbers. Think of it like sifting through clues to find out why profits dipped or why costs soared. It’s essential in finance because it shines a light on performance gaps and helps us steer the ship back on course by analyzing both relative and absolute variances.
Why Combine Power BI Variance Analysis?

Here’s where Power BI and variance analysis become the dynamic duo. By combining forces, you get the analytical prowess of variance analysis with the visualization power of Power BI.
Picture this: you’ve got reams of financial data. Alone, they’re just numbers. But through Power BI, they transform into vibrant charts and graphs that you can actually understand. This fusion allows for real-time insights and smarter decision-making. Whether you’re in retail trying to crack sales puzzles or in manufacturing ironing out cost inefficiencies, Power BI variance analysis is your go-to strategy. It’s like having a crystal ball for financial foresight—minus the hocus pocus.
Setting Up Power BI Variance Analysis
Alright, buckle up, because setting up Microsoft Power BI for variance analysis is like prepping your toolkit before you conquer a mountain. Here’s how we get started.
Prerequisites and Initial Setup
First things first, let’s gather our gear. To get rolling with Power BI, you’ll need:
- Power BI Desktop – Download it from Microsoft’s official site.
- A Data Source – This could be anything from Excel sheets to SQL databases, depending on where your data lives.
Step-by-Step Installation
- Download Power BI Desktop
Head over to the Power BI website, hit that download button, and install it on your machine. It’s as simple as binge-watching your favorite show.
- Sign up for Power BI Services
If you want to share your reports online, signing up for Power BI Services is a good idea. This will allow you to publish and collaborate on your insights.
Connecting Your Data

Time to import your data like a pro. Here’s how you connect the dots:
- Launch Power BI Desktop
Open it up and click on “Get Data.” You’ll see a plethora of options to connect to, from Excel to cloud services like Azure.
- Choose Your Data Source
Select the data source you’re working with. For instance, if your data’s in Excel, choose Excel and locate your file.
- Load Your Data
Hit “Load” and watch as Power BI pulls your data into its realm. This might take a minute, so grab a coffee if you need to.
Ensuring Data Accuracy
Power BI gives you a preview. Check for any anomalies or missing data. Better safe than sorry!
Use the Query Editor to clean your data. You can remove duplicates and filter out irrelevant info here.
Data Modeling Basics

Once your data’s in, it’s time to play matchmaker.
- Access the Model View
Click on “Model” to start building relationships. Think of this as setting up your data’s family tree.
- Create Relationships
Drag and drop to create relationships between tables. If you’ve got, say, a sales table and a returns table, link them through a common field like “Product ID.”
- Set Cardinality
Define how the tables relate to each other. Is it one-to-one, one-to-many? This ensures your data syncs perfectly.
Power BI’s data modeling is like Lego—snap pieces together to build something amazing. And there you have it, the setup phase. You’re now ready to explore variance analysis like a boss!
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting Variance Analysis in Power BI
Get ready to roll up your sleeves because we’re about to create some variance magic in Power BI. Let’s break it down step-by-step.
Use Power BI’s DAX to create a new calculated column for variance values.
Creating Your First Variance Chart
Think of your first variance report as your debut novel—exciting and packed with potential. Here’s how to set it up:
Select Your Data
First, choose the data you want to analyze, including actual values and forecasted sales. For this example, let’s say we’re comparing actual sales to forecasted sales.
Create a New Report
Open Power BI and click on “New Report.” Import your data if you haven’t done so already.
Add a Table or Matrix
Drag and drop fields into a table or matrix variance visual. Place “Actual Sales” and “Forecast Sales” side by side.
Calculate Variance
Use Power BI’s DAX to create a new calculated column. Here’s a simple formula to get you started:
Variance = [Actual Sales] - [Forecast Sales]
Visualize the Variance
Turn your variance into a visual by selecting a bar or line chart. This helps in quickly spotting trends or anomalies.
Use conditional formatting to highlight significant variances. For instance, set red for unfavorable variances and green for favorable ones.
Designing Effective Dashboards with Waterfall Chart
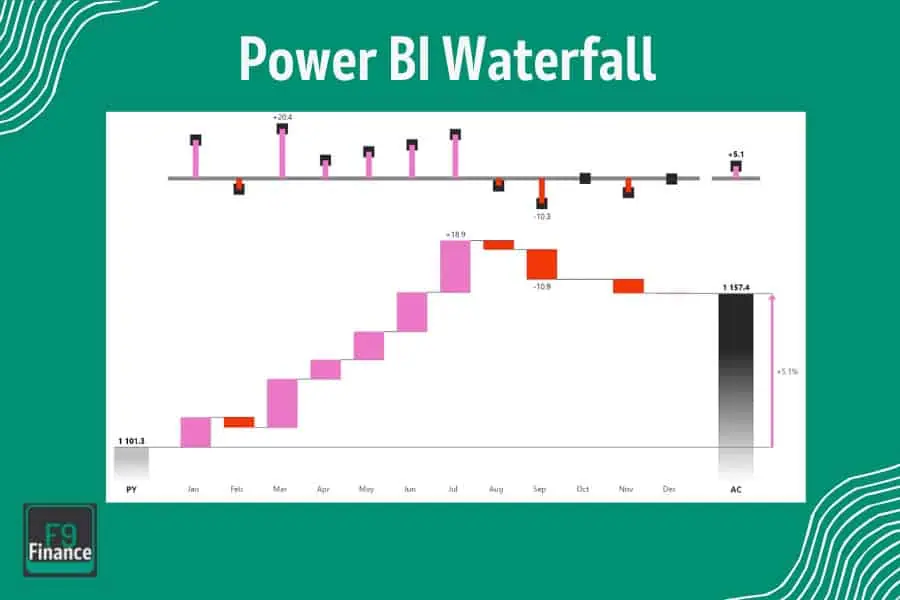
Your dashboard is like the deluxe version of your report—sleek and easy to interpret.
Keep it Simple
Avoid clutter. Focus on key metrics that matter.
Use Card Visuals
Card visuals are great for highlighting important figures like total variance or total sales.
Implement Slicers
Add slicers for easy filtering. This allows users to view data by time period or product category.
Include Trend Lines
Add trend lines to your charts to visualize the variance over time. It’s like adding a storyline to your data. Consider using small multiples to compare multiple sets of data effectively on a single page.
Using DAX for Advanced Calculations
Power BI’s secret sauce is DAX—Data Analysis Expressions. It’s like Excel formulas on steroids.
Intro to DAX
DAX is used to perform calculations and create custom fields, such as comparing actual sales to plan values. It’s powerful yet intuitive once you get the hang of it.
Simple DAX Example
Let’s say you want to calculate percentage variance:
Percentage Variance = DIVIDE([Actual Sales] - [Forecast Sales], [Forecast Sales])
Using DAX for Filters
Use DAX to create calculated filters. For example, only show products with a variance greater than a certain threshold:
Filter = IF([Variance] > 1000, TRUE(), FALSE())
With these steps, you’re all set to conquer variance analysis in Power BI. From building reports to crafting dashboards and harnessing the power of DAX, you’re ready to bring data stories to life. Go forth and analyze with flair!
Real-Life Case Studies
Let’s take a trip into the real world where numbers meet reality, and Power BI shows its true colors. We’ve got two fascinating case studies coming up—one in retail and the other in manufacturing. Buckle up!
Case Study 1: Retail Business
Picture this—a bustling retail chain, “TrendMart,” spread across the country. The objective was to dig into their sales data, identify discrepancies, and uncover untapped opportunities. They were aiming to optimize inventory and improve sales strategies.
Data Collection
TrendMart collected sales data from all their outlets, focusing on comparing sales figures to forecasted sales for the quarter.
Importing Data into Power BI
They imported this data into Power BI, ensuring it was clean and ready for analysis.
Variance Calculation
Using DAX, they calculated sales variance by subtracting forecasted sales from actual sales.
Visualization
They used bar charts to visualize the variance by region and store, making it easier to spot trends and anomalies.
Deep Dive Analysis
With slicers, they filtered the data by product category, seeing which items deviated the most from forecasts.
By analyzing sales variance, TrendMart discovered that certain electronics were consistently underperforming, while apparel exceeded expectations. This insight led to a strategic shift, reallocating resources and adjusting marketing efforts to focus on high-performing categories. The outcome? A significant boost in quarterly earnings and more efficient inventory management.
Case Study 2: Manufacturing Sector
Next up, we have “FabriCo,” a manufacturing giant grappling with escalating production costs. Their goal was to perform a cost variance analysis to pinpoint inefficiencies and streamline operations.
Identifying Cost Elements
FabriCo focused on key cost elements like raw materials, labor, and overheads.
Data Integration
They imported cost data into Power BI, including budgeted, actual, and standard costs from their income statement.
Variance Computation
Using DAX, they calculated cost variances by comparing actual costs against budgeted figures.
Dashboard Creation
They developed a dashboard displaying cost variances, using pie charts and heat maps to highlight areas of concern.
Root Cause Analysis
By drilling down, they discovered that labor costs were spiking due to overtime, and material wastage was higher than expected.
Armed with these insights, FabriCo re-evaluated their production schedules and supplier contracts. By addressing the root causes, they reduced labor costs by 15% and streamlined material usage, ultimately boosting their operational efficiency. The result? A leaner, more cost-effective production line that set the stage for increased profitability.
[ad_2]




